How to Get Rid of Gridlines in Pixel Art Ai
- Illustrator User Guide
- Get to know Illustrator
- Introduction to Illustrator
- What's new in Illustrator
- Mutual questions
- Illustrator system requirements
- Illustrator for Apple silicon
- Workspace
- Workspace nuts
- Create documents
- Tools
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Introduction to artboards
- Manage artboards
- Customize the workspace
- Properties console
- Set preferences
- Affect Workspace
- Microsoft Surface Dial support in Illustrator
- Recovery, undo, and automation
- Rotate view
- Rulers, grids, and guides
- Accessibility in Illustrator
- Safe Mode
- View artwork
- Use the Impact Bar with Illustrator
- Files and templates
- Synchronize settings using Adobe Creative Cloud
- Tools in Illustrator
- Selection
- Overview
- Selection
- Direct Selection
- Lasso
- Artboard
- Navigation
- Overview
- Zoom
- Rotate View
- Paint
- Overview
- Gradient
- Shape Builder
- Type
- Overview
- Type
- Blazon on Path
- Selection
- Introduction to Illustrator
- Illustrator on the iPad
- Introduction to Illustrator on the iPad
- Illustrator on the iPad overview
- Illustrator on the iPad FAQs
- Organization requirements | Illustrator on the iPad
- What y'all can or cannot do on Illustrator on the iPad
- Workspace
- Illustrator on the iPad workspace
- Touch shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts for Illustrator on the iPad
- Manage your app settings
- Documents
- Work with documents in Illustrator on the iPad
- Import Photoshop and Fresco documents
- Select and arrange objects
- Create repeat objects
- Blend objects
- Drawing
- Draw and edit paths
- Draw and edit shapes
- Type
- Piece of work with type and fonts
- Create text designs along a path
- Add your own fonts
- Work with images
- Vectorize raster images
- Colour
- Utilise colors and gradients
- Introduction to Illustrator on the iPad
- Deject documents
- Basics
- Piece of work with Illustrator cloud documents
- Share and collaborate on Illustrator cloud documents
- Upgrade cloud storage for Adobe Illustrator
- Illustrator cloud documents | Common questions
- Troubleshooting
- Troubleshoot create or save issues for Illustrator cloud documents
- Troubleshoot Illustrator deject documents problems
- Basics
- Add and edit content
- Drawing
- Drawing basics
- Edit paths
- Draw pixel-perfect art
- Draw with the Pen, Curvature, or Pencil tool
- Draw simple lines and shapes
- Image Trace
- Simplify a path
- Define perspective grids
- Symbolism tools and symbol sets
- Adjust path segments
- Blueprint a flower in v like shooting fish in a barrel steps
- Perspective drawing
- Symbols
- Draw pixel-aligned paths for web workflows
- 3D effects and Adobe Substance materials
- About 3D furnishings in Illustrator
- Create 3D graphics
- Map artwork over 3D objects
- Create 3D objects
- Create 3D Text
- About 3D furnishings in Illustrator
- Color
- Most colour
- Select colors
- Employ and create swatches
- Adjust colors
- Use the Adobe Color Themes console
- Colour groups (harmonies)
- Color Themes panel
- Recolor your artwork
- Painting
- About painting
- Pigment with fills and strokes
- Live Paint groups
- Gradients
- Brushes
- Transparency and blending modes
- Apply stroke on an object
- Create and edit patterns
- Meshes
- Patterns
- Select and adapt objects
- Select objects
- Layers
- Grouping and aggrandize objects
- Move, align, and distribute objects
- Stack objects
- Lock, hibernate, and delete objects
- Indistinguishable objects
- Rotate and reverberate objects
- Reshape objects
- Crop images
- Transform objects
- Combine objects
- Cut, separate, and trim objects
- Puppet Warp
- Calibration, shear, and misconstrue objects
- Alloy objects
- Reshape using envelopes
- Reshape objects with effects
- Build new shapes with Shaper and Shape Builder tools
- Work with Alive Corners
- Enhanced reshape workflows with touch support
- Edit clipping masks
- Live shapes
- Create shapes using the Shape Builder tool
- Global editing
- Type
- Add together text and work with blazon objects
- Manage text area
- Fonts and typography
- Format type
- Import and export text
- Format paragraphs
- Special characters
- Create type on a path
- Character and paragraph styles
- Tabs
- Text and type
- Notice missing fonts (Typekit workflow)
- Update text from Illustrator 10
- Arabic and Hebrew blazon
- Fonts | FAQ and troubleshooting tips
- Create 3D text upshot
- Creative typography designs
- Scale and rotate type
- Line and character spacing
- Hyphenation and line breaks
- Text enhancements
- Spelling and linguistic communication dictionaries
- Format Asian characters
- Composers for Asian scripts
- Create text designs with blend objects
- Create a text poster using Image Trace
- Create special effects
- Work with furnishings
- Graphic styles
- Create a driblet shadow
- Appearance attributes
- Create sketches and mosaics
- Driblet shadows, glows, and feathering
- Summary of effects
- Spider web graphics
- All-time practices for creating web graphics
- Graphs
- SVG
- Create animations
- Slices and image maps
- Drawing
- Import, export, and save
- Import
- Import artwork files
- Import bitmap images
- Import artwork from Photoshop
- Place multiple files | Illustrator CC
- Unembed images
- Import Adobe PDF files
- Import EPS, DCS, and AutoCAD files
- Links information
- Creative Cloud Libraries in Illustrator
- Creative Deject Libraries in Illustrator
- Save
- Salve artwork
- Export
- Apply Illustrator artwork in Photoshop
- Export artwork
- Collect avails and consign in batches
- Package files
- Create Adobe PDF files
- Extract CSS | Illustrator CC
- Adobe PDF options
- File data and metadata
- Import
- Press
- Set up for printing
- Ready documents for printing
- Modify the page size and orientation
- Specify crop marks for trimming or aligning
- Get started with large canvass
- Printing
- Overprint
- Impress with colour management
- PostScript printing
- Print presets
- Printer'southward marks and bleeds
- Impress and salvage transparent artwork
- Trapping
- Print color separations
- Impress gradients, meshes, and colour blends
- White Overprint
- Set up for printing
- Automate tasks
- Information merge using the Variables console
- Automation with scripts
- Automation with actions
- Troubleshooting
- Crash issues
- Recover files subsequently crash
- File bug
- GPU device commuter issues
- Wacom device issues
- DLL file issues
- Retentivity bug
- Preferences file bug
- Font issues
- Printer bug
- Share crash report with Adobe
Use rulers
Rulers help you accurately identify and measure objects in the illustration window or in an artboard. The point where 0 appears on each ruler is called the ruler origin.
Illustrator provides carve up rulers for documents and artboards. You can select only one of these rulers at a time.
Global rulers appear at the top and left sides of the analogy window. The default ruler origin is located at the superlative-left corner of the illustration window.
Artboard rulers appear at the top and left sides of the active artboard. The default artboard ruler origin is located at the top-left corner of the artboard.
The divergence between artboard rulers and global rulers is that if y'all select artboard rulers, the origin betoken changes based on the active artboard. In improver, you can have different origin points for artboard rulers. Now, if yous change the artboard ruler origin, the blueprint fills in objects on the artboards are non affected.
The default origin point for the global ruler is at the upper-left corner of the first artboard and the default origin for the artboard rulers is at the pinnacle left corner of the respective artboard.
- To show or hide rulers, choose View > Rulers > Show Rulers or View> Rulers > Hide Rulers.

-
To toggle between artboard rulers and global rulers, choose View > Rulers > Change to Global Rulers or View > Rulers > Change to Artboard Rulers. Artboard rulers announced by default, so the Alter to Global Rulers option appears in the Rulers sub-menu.
-
To testify or hide video rulers, cull View > Show Video Rulers or View > Hide Video Rulers.
-
To change the ruler origin, move the pointer to the upper-left corner where the rulers intersect, and drag the pointer to where you want the new ruler origin.
As you lot elevate, a cross hair in the window and in the rulers indicates the changing global ruler origin.
Notation: Irresolute the global ruler origin affects the tiling of patterns.
-
To restore the default ruler origin, double-click the upper-left corner where the rulers intersect.
The coordinate system has now been switched to fourth quadrant, which was previously the first quadrant. In Illustrator CS5, when you move downwards, the value of y-axis increases and if you move toward correct, the value of x-centrality increases.
For saving to legacy versions of Illustrator, the Global rulers remain at the position set in legacy document. Although, the origin point does not move to upper left, the coordinate arrangement changes to 4th quadrant.
The change in coordinate system and the ruler origin does not utilize to scripting, which allows y'all to retain old scripts. However, when you transform objects using scripting, the Y coordinate values differ from the values that you prepare in the Illustrator user interface. For case, if y'all apply a movement operation of say Y= +x points, and so to emulate the aforementioned motion with scripting, apply a transformation of Y = -10pts.
Change the unit of measurement of measurement
The default unit in Illustrator is points (a point equals .3528 millimeter). Y'all tin can change the unit of measurement that Illustrator uses for full general measurements, strokes, and type. You can override the default unit while inbound values in boxes.
- To change the default unit, choose Edit > Preferences > Units (Windows) or Illustrator > Preferences > Units (Mac OS), and so select units for the General, Stroke, and Type options. If Evidence Asian Options is selected in the Blazon preferences, you tin can also select a unit specifically for Asian blazon.
Notation: The General measurement option affects rulers, measuring the altitude betwixt points, moving and transforming objects, setting grid and guides spacing, and creating shapes.
- To ready the full general unit of measurement for the current document only, choose File > Document Setup, cull the unit you want to use from the Units menu, and click OK.
- To change the unit of measurement of measurement when entering a value in a box, follow the value by whatsoever of the following abbreviations: inch, inches, in, millimeters, millimetres, mm, Qs (ane Q equals 0.25 millimeter), centimeters, centimetres, cm, points, p, pt, picas, pc, pixel, pixels, and px.
Tip: When mixing picas and points, you tin can enter values as XpY, where X and Y are the number of picas and points (for example, 12p6 for 12 picas, 6 points).
Employ the grid
The filigree appears behind your artwork in the analogy window. It does not print.
- To show or hibernate the grid, choose View > Show Grid or View > Hide Grid.
- To snap objects to gridlines, cull View > Snap To Grid, select the object yous want to motility, and elevate it to the desired location.
When the object's boundaries come within 2 pixels of a gridline, it snaps to the point.
Note: If you cull View > Pixel Preview, Snap To Grid changes to Snap To Pixel.
- To specify the spacing between gridlines, grid style (lines or dots), grid color, or whether grids announced in the front end or back of artwork, choose Edit > Preferences > Guides & Grid (Windows) or Illustrator > Preferences > Guides & Grid (Mac Os).

Employ guides
Guides assist you align text and graphic objects. Yous can create ruler guides (straight vertical or horizontal lines) and guide objects (vector objects that you convert to guides). Like the grid, guides do not impress.
You tin choose between ii guide styles—dots and lines—and you lot can change the color of guides by using either predefined guide colors or colors you select using a color picker. By default, guides are unlocked so that yous can motion, modify, delete, or revert them, but you tin can choose to lock them into identify.
- To show or hide guides, choose View > Guides > Evidence Guides or View > Guides > Hide Guides.
- To change guide settings, choose Edit > Preferences > Guides & Grid (Windows) or Illustrator > Preferences > Guides & Grid (Mac Bone).
- To lock guides, select View > Guides > Lock Guides.
Create guides
-
If the rulers aren't showing, choose View > Evidence Rulers.
-
Position the pointer on the left ruler for a vertical guide or on the summit ruler for a horizontal guide.
-
Drag the guide into position.
To convert vector objects to guides, select them and choose View > Guides > Make Guides.
To make working with multiple guides easier, move them into a split up layer.
-
To restrict the guides to an artboard instead of the entire canvas, select the Artboard tool and elevate the guides on to the artboard.
Move, delete, or release guides
-
If guides are locked, select View > Guides > Lock Guides.
-
-
To motility the guide, elevate it or copy it.
-
To delete the guide, press the backspace fundamental (Windows) or the Delete primal (Mac Os), or choose Edit > Cut or Edit > Articulate.
-
To delete all guides at once, choose View > Guides > Clear Guides.
-
To release the guide, turning information technology back into a regular graphic object, select the guide and cull View > Guides > Release Guides.
-
Snap objects to ballast points and guides
-
Cull View > Snap To Point.
-
Select the object you want to move, and position the pointer on the exact bespeak you want to align with anchor points and guides.
When snapping to a point, the snapping alignment depends on the position of the arrow, not the edges of the dragged object.
-
Drag the object to the desired location.
When the pointer comes within 2 pixels of an anchor point or guide, it snaps to the signal. When a snap occurs, the arrow changes from a filled arrowhead to a hollow arrowhead.
Use Smart Guides
Smart Guides are temporary snap‑to guides that announced when yous create or dispense objects or artboards. They help you marshal, edit, and transform objects or artboards relative to other objects, artboards, or both by snap-adjustment and displaying X, Y location, and delta values. Y'all can specify the type of smart guides and feedback that appear (such as measurement labels, object highlighting, or labels) by setting the Smart Guides preferences.
Smart Guides are on by default.
-
To turn Smart Guides on or off, choose View > Smart Guides.
-
Use Smart Guides in the following ways:
-
When yous create an object with the pen or shape tools, use the Smart Guides to position a new object's anchor points relative to an existing object. Or, when yous create a new artboard, use Smart Guides to position it relative to another artboard or an object.
-
When yous create an object with the pen or shape tools, or when you transform an object, employ the Smart Guides' construction guides to position ballast points to specific preset angles, such as 45 or xc degrees. Specify these angles in the Smart Guides preferences.
-
When yous move an object or artboard, use the Smart Guides to align the selected object or artboard to other objects or artboards. The alignment is based on the geometry of objects and artboards. Guides announced equally the object approaches the edge or center bespeak of other objects.
-
When you transform an object, Smart Guides automatically appear to assistance the transformation.
You tin change when and how Smart Guides appear by setting Smart Guides preferences.
When Snap To Grid or Pixel Preview is turned on, y'all can't utilize Smart Guides (even if the menu command is selected).
-
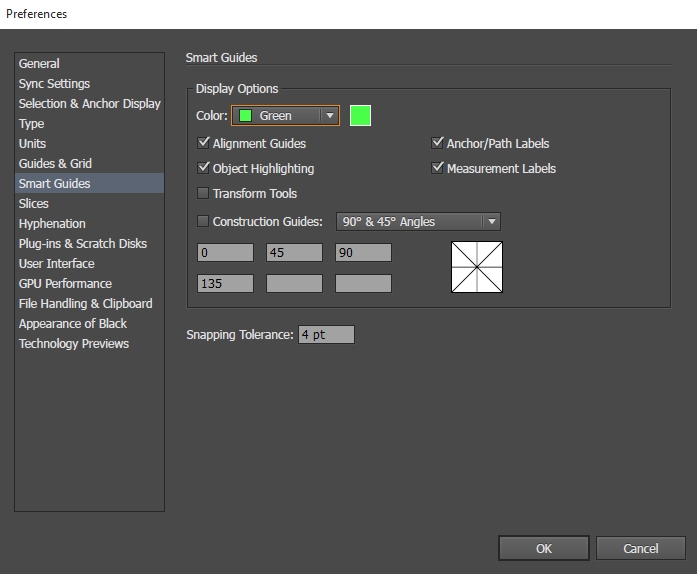
Set Smart Guides preferences
Cull Edit > Preferences > Smart Guides (Windows) or Illustrator > Preferences > Smart Guides (Mac OS) to fix the following preferences:
Colour
Specifies the color of the guides.
Alignment Guides
Displays guide lines that are generated along the centre and edges of geometric objects, artboard, and bleeds. They are generated when you move objects and when you perform operations such equally cartoon basic shapes, using the Pen tool, and transforming objects.
Ballast/Path Labels
Displays information when paths intersect and when they are centered on an anchor indicate.
Measurement Labels
Displays information for many tools (such every bit Drawing tools and Text tools) about the position of the cursor as you position the cursor over an anchor point. While you create, select, move, or transform objects, information technology displays the x and y delta from the object's original location. When you press Shift with a cartoon tool selected, the starting location appears.
Object Highlighting
Highlights the object below the arrow as yous elevate around it. The highlight colour matches the object'south layer colour.
Transform Tools
Displays data when you scale, rotate, and shear objects.
Construction Guides
Displays guidelines as you draw new objects. You lot specify the angles at which you desire guidelines drawn from the anchor points of a nearby object. You can prepare to six angles. Enter an angle in the selected Angles box, select a ready of angles from the Angles pop‑up menu, or select a set of angles from the pop‑upward menu and alter one of the values in the box to customize a ready of angles. The preview reflects your settings.
Snapping Tolerance
Specifies the number of points the pointer must be from another object for Smart Guides to have effect.
Measure distance between objects
Use the Measure tool to calculate the distance between any two points and display the results in the Info panel.
-
Select the Measure tool
 . (Select and hold the Eyedropper tool to run into information technology in the Tools panel.)
. (Select and hold the Eyedropper tool to run into information technology in the Tools panel.) -
-
Click the two points to mensurate the distance betwixt them.
-
Click the first point and drag to the 2d bespeak. Shift‑drag to constrain the tool to multiples of 45°.
The Info panel displays the horizontal and vertical distances from the ten and y axes, the accented horizontal and vertical distances, the total distances, and the angle measured.
-
Navigate the Info panel
Employ the Info panel (Window > Info) to get data on the area beneath the pointer and on selected objects.
-
When an object is selected and a pick tool is active, the Info panel displays the object'southward ten and y coordinates, width (Westward), and height (H). The values for width and height are afflicted by the Use Preview Bounds option in the General preferences. When Use Preview Premises is selected, Illustrator includes the stroke width (and other attributes such every bit drop shadows) in the object'due south dimensions. When Use Preview Premises is cleared, Illustrator measures only the dimensions defined by the object's vector path.
-
When you use the Pen tool or Gradient tool, or when y'all move a selection, the Info panel displays the change in x (W), the alter in y (H), the altitude (D), and the angle
 as you drag.
as you drag. -
When y'all employ the Zoom tool, the Info panel displays the magnification gene and the x and y coordinates after you release the mouse button.
-
When you use the Calibration tool, the Info console displays the percentage change in width (W) and superlative (H) and the new width (W) and height (H) after the scaling is complete. When yous utilize the rotate or reflect tools, the Info panel displays the coordinates of the object's eye and the angle of rotation
 or reflection
or reflection .
. -
When you use the Shear tool, the Info panel displays the coordinates of the object'southward heart, the angle of shear axis
 , and the amount of shear
, and the amount of shear .
. -
When you use the Paintbrush tool, the Info panel displays the x and y coordinates and the proper name of the current castor.
-
Select Show Options from the panel carte or click the double arrow on the panel tab to brandish values for the fill and stroke colors of the selected object and the name of any pattern, gradient, or tint applied to the selected object.
Note: If you select multiple objects, the Info panel displays only the information that is the aforementioned for all selected objects.
More than like this
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/illustrator/using/rulers-grids-guides-crop-marks.html

0 Response to "How to Get Rid of Gridlines in Pixel Art Ai"
Post a Comment